What is Anxiety ?
Anxiety represents a blend of mental and physical reactions to negative anticipation. On a psychological level, it often involves heightened alertness and apprehension, spiralling into distressing worry. Physically, it manifests as discomfort due to the activation of several bodily systems, all aimed at preparing for an uncertain threat, whether actual or imagined.
Feelings of dread and physical symptoms like a racing heart and jitteriness are mechanisms designed to create unease. These responses help us focus and drive necessary actions to safeguard our well-being. Feeling anxious from time to time is a normal aspect of life and can actually be helpful, as it encourages us to think ahead about what might happen. On the other hand, when anxiety becomes too intense or is not properly managed, it can lead to issues.
Why Is Anxiety Increasing in Children Day by Day?
Anxiety among children is rising due to multiple factors. Overprotective parenting and high expectations limit resilience, while academic pressure intensifies stress. Technology and social media expose children to cyberbullying, negative comparisons, and FOMO, amplifying their anxiety. Global uncertainties like climate change and pandemics heighten fears, while reduced social interactions and sedentary lifestyles hinder emotional development. Sleep deprivation and family stress further exacerbate the problem. To combat this, parents must foster open communication, encourage physical activity, and promote resilience through problem-solving. Setting healthy digital boundaries and seeking professional help when needed can help children manage anxiety and lead balanced lives.
When Does Anxiety Become a Disorder?
Overwhelming anxiety that disrupts daily routines be it at work, school, or in social settings is classified as an anxiety disorder. Studies reveal that nearly one third of adults in the world experience excessive anxiety at some stage in their lives.
Anxiety often coexists with depression, as both conditions share similar symptoms and branch of medicine that deals with problems affecting the nervous system pathways. Various factors, including biological, early childhood experiences and overprotective parenting styles, contribute to the development of anxiety disorders.
it is unlikely that you will be able to eliminate your anxiety forever. Effective treatment focuses on managing anxiety levels. Approaches like therapy, medication, regular exercise, and deep breathing exercises play crucial roles in maintaining balance.
Why Is Anxiety Increasing?
Anxiety has emerged as the most prevalent mental health challenge globally, with rates continuing to rise, particularly among young people. Increasing numbers of children and adolescents are being diagnosed with anxiety disorders.
One significant reason for this rise is the growing uncertainty in nearly all aspects of modern life, driven by economic and cultural changes. Although uncertainty itself does not directly cause anxiety, it creates an environment where anxiety can thrive.
In younger individuals, factors like overprotective parenting and the influence of social media play significant roles. While technology enables connection, it also introduces negative comparisons and avenues for social exclusion, exacerbating anxiety.
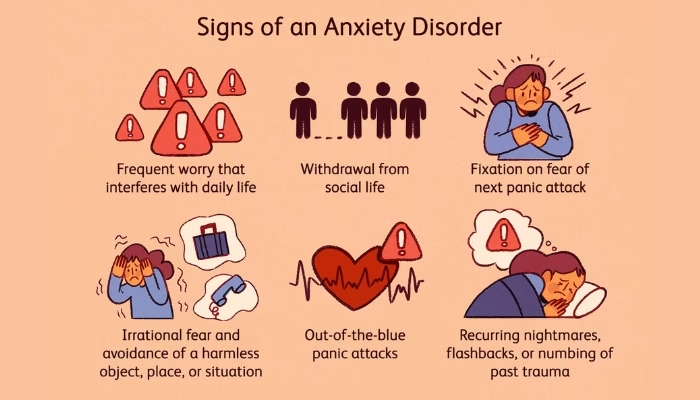
Recognising the Signs of Anxiety
Anxiety often manifests through relentless cycles of worry and physical discomfort. Symptoms may include trembling, rapid heartbeats, shortness of breath, and general restlessness.
Physical symptoms can sometimes be misinterpreted, such as mistaking anxiety induced chest discomfort for a heart attack. This often leads to misdiagnosis, delaying proper treatment. Identifying anxiety’s root cause is essential for effective management.
Anxiety in Children
Approximately one in eight children experience significant anxiety. Common worries include separation from parents, natural disasters, and global issues like climate change. Anxiety becomes problematic when it disrupts activities like school attendance or social interaction. Overprotective parenting styles often contribute to heightened anxiety levels in children.
Managing Anxiety
Effective management of anxiety disorders typically involves a combination of psychotherapy, medication, and lifestyle adjustments. Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) is a highly effective treatment tailored to address specific anxieties. It equips individuals with tools to challenge distorted thoughts and gradually face their fears.
Exposure therapy, where individuals confront their fears in controlled environments, is a key element of many anxiety treatments. Medications can also aid in symptom management, enabling individuals to engage more fully in therapy.
Lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, mindfulness practices, and controlled breathing techniques, play a pivotal role in long-term anxiety control.
When Is Anxiety Considered an Illness?
Experiencing anxiety occasionally is a natural part of life. However, it becomes a disorder when it occurs without a clear cause, is disproportionate to the triggering situation, or persists even after resolving potential problems. Anxiety disorders are have as a typical quality by excessive mental preoccupation and avoidance behaviours, impacting daily functioning and overall well being.
Different Forms of Anxiety
Anxiety presents in various forms, each with unique characteristics. Generalised Anxiety Disorder (GAD) involves persistent concerns across major life areas like work, relationships, and health. Social Anxiety Disorder focuses on the fear of being judged negatively, which is increasingly prevalent among young adults.
Phobias are intense fears centred on specific objects or Strongest matches. Panic attacks, characterised by sudden and overwhelming feelings of terror, can occur unpredictably or frequently, severely impacting daily life. Fortunately, all forms of anxiety are treatable with proper care.
Understanding the Causes of Anxiety
At its core, anxiety derive, emanates, flows, issue, originate, proceed, rise, spring, and stems from our ability to imagine the future. Uncertainty often fuels anxiety, making today’s expected before it happens world a fertile ground for it. Triggers can range from real world events like relationship issues and financial stress to internal fears stemming from imagined scenarios.
Best Therapies for Anxiety
Behavioural therapy is considered the gold standard for treating anxiety. By focusing on practical solutions, Cognitive Behavior Therapy helps individuals identify and counteract distorted thought patterns, providing tools to manage reactivity and restore emotional balance.
Therapy sessions offer the added benefit of human connection, which is crucial for calming overactive nervous systems. A supportive environment during therapy serves as a reassuring signal of safety, helping counter the sense of threat central to anxiety disorders.
Natural Remedies for Anxiety
Managing anxiety often doesn’t necessitate medication. There are many natural methods that can greatly ease symptoms. Meditation, which has its roots in Eastern traditions, is effective in calming the mind. Engaging in physical activities such as walking or running helps to relieve muscle tension and enhances mental clarity. Deep breathing, also known as diaphragmatic breathing, directly calms the nervous system and reduces feelings of threat.
Biological Aspects of Anxiety
Anxiety triggers a cascade of hormonal responses affecting multiple bodily systems. While the mental state becomes hyper alert to potential danger, physical symptoms like jitteriness and muscle tension prepare the body for action, a mechanism designed to protect against perceived threats.
Vulnerability hangovers often result in anxiety
Anyone can experience debilitating anxiety under certain conditions. Genetic something likely to behave in a particular way or suffer from a medical condition, early life experiences, and heightened brain activity in specific regions can make some individuals more prone to anxiety. Stress is another significant factor, often overlapping with and exacerbating anxiety.
Understanding Panic Attacks
Panic attacks are sudden episodes of intense anxiety that can feel life-threatening. Symptoms include rapid heartbeat, difficulty breathing, and overwhelming terror. While alarming, these attacks can be managed with proper techniques, even during an episode.
Anxiety in Children
Approximately one in eight children experience significant anxiety. Common worries include separation from parents, natural disasters, and global issues like climate change. Anxiety becomes problematic when it disrupts activities like school attendance or social interaction. Overprotective parenting styles often contribute to heightened anxiety levels in children.
Conclusion
Anxiety is a natural response but becomes posing a problem when persistent. Rising cases, especially in children, stem from protect someone, especially a child, too much parenting, academic pressure, and social media. Early recognition, therapy, and lifestyle changes can help manage it. Visit Vicimantra for more strategies.